


Traditional Marketing vs Digital Marketing: Which one is better?
November 2, 2023


Starting from Scratch: How to Successfully Enter the E-commerce Industry – Part 2
December 1, 2023Starting from Scratch: How to Successfully Enter the E-commerce Industry - Part 1
Table of Contents

Chapter 1: Introduction to E-commerce
E-commerce, commonly abbreviated as e-commerce, refers to the process of conducting business activities and transactions through the Internet and digital technologies. It encompasses various business activities such as online shopping, digital marketing, website development, logistics, and supply chain management. The core objective of e-commerce is to facilitate the sale of products and services and achieve business goals.
E-commerce holds a significant position in modern business, driven by the importance of several aspects:
- Global Opportunities: E-commerce eliminates geographical restrictions, allowing businesses to reach global markets. It provides opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises to enter international markets and expand their customer base.
- 24/7 Operations: E-commerce websites can provide services at any time, operating around the clock, allowing consumers to shop according to their schedules. This enhances customer convenience and promotes sales.
- Cost Reduction: Maintaining and operating an e-commerce website is generally more cost-effective compared to traditional brick-and-mortar stores. This includes reduced rent, labor costs, and inventory costs.
- Customer Data Analysis: E-commerce enables businesses to collect customer data and analyze their behaviors and preferences. This data can be used for personalized marketing and providing a better customer experience.
- Digital Marketing: E-commerce has fostered the development of digital marketing, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, content marketing, and more. These strategies help businesses attract traffic and increase online visibility.
- Multi-Channel Sales: Businesses can sell through various online channels, such as their own website, social media platforms, marketplaces, and more, expanding their market coverage.
In summary, e-commerce has become an integral part of modern business, offering more opportunities, efficiency, and greater market influence. It benefits not only businesses but also provides consumers with more choices and convenience, playing a crucial role in today’s business environment.
E-commerce exists in various forms, and these forms primarily depend on the entities involved in transactions. Here are some common forms of e-commerce:
- B2B (Business-to-Business): B2B e-commerce refers to the process of transactions between businesses. In this form, one business (supplier) can engage in transactions with another business (customer) for the exchange of products or services. This form typically involves bulk transactions, such as the purchase of raw materials, supply chain management, and collaboration agreements.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): B2C e-commerce involves businesses selling products or services directly to individual consumers. This is the most common form of e-commerce, covering areas such as online retail, subscription services, digital downloads, and online ordering. In the B2C model, businesses interact directly with end consumers and usually sell their goods through online stores or marketplaces.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): C2C e-commerce allows individual consumers to engage in transactions with each other, where they can sell their own items to other individuals. This form typically occurs on online marketplaces or auction websites, such as eBay. Individuals can sell used goods, homemade products, or items they no longer need, providing a platform for small-scale business transactions.
- B2G (Business-to-Government): B2G e-commerce involves businesses selling products or services to government agencies. This form includes government contracts, public procurement, and government purchasing. Businesses may offer various services, such as information technology, construction projects, healthcare, etc., to meet government needs.
- P2P (Peer-to-Peer): P2P e-commerce refers to direct transactions between individuals without involving businesses or intermediaries. This includes sharing economy platforms like Airbnb and Uber, where individuals share their assets or provide services in exchange for income.
- O2O (Online-to-Offline): O2O e-commerce is a model that integrates online and offline elements. It includes online search and ordering, but the actual product or service is provided offline. Examples include restaurant reservations, ticket purchases, and local service bookings.
These different forms of e-commerce provide various choices for different types of transactions and participants. Each form has its unique characteristics and challenges, playing a crucial role in the modern business environment. Businesses and consumers can choose the most suitable e-commerce form based on their needs and objectives.
The rapid growth and potential of the e-commerce market are noteworthy features in today’s business landscape. Here are key perspectives emphasizing the importance and potential of the e-commerce market:
- Global Market Potential: With the widespread adoption of the internet and the global trend toward digitization, the e-commerce market has become a part of the global economy. It provides opportunities for businesses to expand their market scale, regardless of their geographical location.
- Consumer Convenience: E-commerce offers consumers the convenience of shopping without leaving their homes. This enables consumers to access products and services anytime, anywhere, facilitating a personalized shopping experience.
- Innovation and Digital Technology: The e-commerce market is filled with innovation and opportunities due to continuous technological advancements. Emerging technologies such as virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and blockchain are changing the landscape of e-commerce, providing businesses with tools to enhance efficiency and customer experiences.
- Diverse Business Models: The e-commerce market encompasses various business models, including online retail, subscription services, the sharing economy, cross-border e-commerce, and more. This diversity provides businesses with different choices to adapt to various market demands.
- Data Analysis and Personalized Marketing: E-commerce enables businesses to collect extensive customer data and leverage data analysis for improved personalized marketing. This contributes to increased sales and customer loyalty.
- Opportunities for Small Businesses: E-commerce presents an opportunity for small businesses to enter the market without the need for expensive physical storefronts. This expansion diversifies the competitive landscape, allowing more businesses to participate.
In conclusion, the rapid growth and potential of the e-commerce market make it an indispensable part of modern business. Both businesses and consumers benefit significantly in this digital age, and e-commerce will continue to evolve and innovate to meet the ever-changing demands and opportunities. Whether large enterprises or small startups, all can participate in this market with limitless potential.


Chapter 2: Preparation
1. Choose a Product or Service:
Selecting a product or service with market demand is a key element of successful entrepreneurship. Here are steps to help you identify and choose a popular product or service:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand current trends and demand. Study competitors to know what products or services they offer and identify market gaps.
- Target Audience: Determine your target audience, their needs, and preferences. Understanding characteristics such as age, gender, location, and income level can help position your product or service effectively.
- Assess Market Demand: Evaluate market demand to see if there’s sufficient interest in your offering. This can be done through surveys, focus group discussions, online research, and other methods.
- Problem Solving or Meeting Needs: Your product or service should address a real-life problem or fulfill a need. People typically purchase products or services to enhance their quality of life or meet a specific need.
- Unique Value Proposition: Ensure your product or service has a unique value proposition, making it stand out in a competitive market. Uniqueness can be in terms of product quality, pricing, customer service, innovation, and more.
- Feasibility Analysis: Conduct a feasibility analysis to determine if you have enough resources and capabilities to start this business. Consider financial, operational, marketing, and legal requirements.
- Test the Market: Before a full launch, test your product or service on a small scale. This helps you gauge market response and make necessary adjustments.
- Build Brand and Marketing Strategy: Once market demand is established, begin building your brand and marketing strategy. This includes website development, social media marketing, advertising campaigns, and more.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment: The market environment is dynamic. Continuously monitor market feedback and adjust your product or service to meet new needs and trends.
Choosing a product or service with a strong market demand takes time and effort. Once you identify a viable opportunity, you’ll be on your way to building a successful business. Remember, the key is understanding the market to ensure your product or service meets customer needs and provides value.
Market research and competitive analysis are key steps in the success of business operations, and their importance is reflected in several aspects:
- Understanding the Target Market: Market research helps you delve into understanding your target market, including its size, growth trends, consumer demands, and characteristics. This aids in determining the market’s potential and positioning your product or service within that market.
- Identifying the Target Audience: Through market research, you can identify and target your audience more effectively. Understanding their characteristics, needs, and behaviors helps better meet their expectations and formulate targeted marketing strategies.
- Discovering Market Demand and Trends: Through market research, you can identify current market demands and trends. This enables you to adjust your product or service to meet these demands and adapt to changes in the market.
- Competitive Analysis: Understanding the competitive environment is crucial. Competitive analysis helps identify competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, as well as opportunities and threats in the market. This assists in formulating effective competitive and differentiation strategies.
- Risk Reduction: Market research helps reduce business risks by aiding in making informed decisions, lowering the likelihood of failure. This helps save time and resources, ensuring the success of your business.
- Customer Insights: Market research provides customer insights, enabling a better understanding of customer needs, expectations, and satisfaction. This helps provide a better customer experience and build long-term customer relationships.
- Innovation and Development: Market research aids in discovering new opportunities and innovative ideas to meet market demands. This contributes to the long-term development and competitive advantage of the business.
In conclusion, market research and competitive analysis are the cornerstones of business success. They provide valuable information to make informed decisions, ensuring that your product or service meets market demands and stands out in a competitive environment.
2. Create a Business Plan
A business plan is a crucial tool for the success and development of a business. Here’s why you need a business plan and how to create an effective one:
Why You Need a Business Plan:
- Guidance and Direction: A business plan provides a clear guide, helping businesses determine goals, priorities, and development directions. It ensures that the team works towards common objectives and maintains consistency.
- Fundraising: If you need to raise funds, such as loans or investments, a comprehensive business plan is crucial. Investors and lenders often require a plan to assess the feasibility and potential of your business.
- Risk Management: A business plan helps identify potential risks and issues, allowing you to formulate strategies to address them. This aids in reducing uncertainty when the business encounters problems.
- Market Analysis: Through market research and analysis, a business plan helps you understand market demands, competitive environments, and opportunities. This assists in formulating effective market strategies.
- Goal Setting: A business plan helps you determine long-term and short-term goals, along with strategies and plans to achieve these goals.
How to Create an Effective Business Plan:
- Clear Executive Summary: Provide a concise executive summary at the beginning of the plan, outlining the core aspects of your business, including the business model, goals, and competitive advantages.
- Market Analysis: Conduct detailed market research, including the target market, competitive analysis, and trend forecasts. Ensure you have a deep understanding of the market.
- Product or Service Description: Clearly describe your product or service, including its features, advantages, and pricing strategy.
- Marketing Strategy: Develop a marketing plan, including advertising, sales, and brand promotion strategies. Discuss how to attract customers and promote business growth.
- Financial Plan: Provide financial forecasts, including income, expenses, profitability, and cash flow. This helps assess the financial feasibility of the business.
- Team and Operations: Describe your team structure, management model, and operational plans. This includes the supply chain, facilities, and operational processes.
- Risk Analysis: Identify potential risks and issues, providing strategies to address them. This demonstrates your awareness of business challenges and your ability to cope.
- Timeline and Milestones: Develop a timeline, including key milestones and target achievement times. This helps track progress.
- Review and Update: A business plan should be a living document, requiring constant review and updates to reflect changes in the market and business needs.
In conclusion, an effective business plan is a key tool that helps determine the success and sustainability of a business. It not only provides a clear roadmap but also aids in attracting investors, managing risks, understanding the market, and achieving business goals.
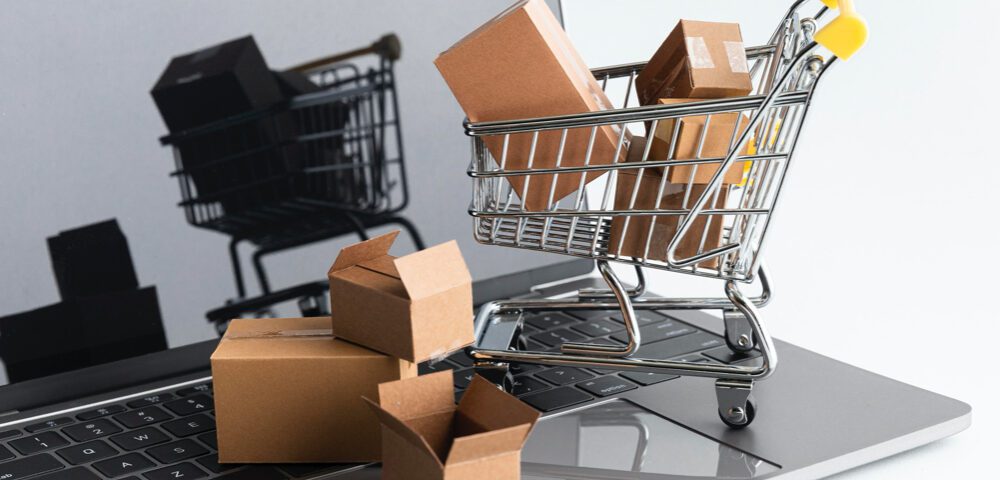


Chapter 3: Establishing Online Presence
1. Choose a Domain Name and Hosting
Establishing an online presence begins with selecting an appropriate domain name and hosting. Here are some recommendations:
Choosing a Domain Name:
- Relevance to Business: Choose a domain name that is relevant to your business, making it easy for people to understand what your business is about. This contributes to building brand identity.
- Short and Memorable: Opt for a concise, easy-to-pronounce, and memorable domain name to facilitate recall.
- Select Appropriate Domain Extension: Common domain extensions include .com, .net, .org, etc. Choose an extension that suits your business; generally, .com is the most popular.
- Avoid Special Characters and Hyphens: Minimize the use of special characters and hyphens in your domain name to enhance usability.
- Consider Keywords: If possible, include some relevant keywords in your domain name. This can aid in search engine optimization (SEO).
Choosing Hosting:
- Reliability and Performance: Choose a hosting provider that offers high reliability and superior performance. Check their Service Level Agreement (SLA) to ensure your website remains stable during operation.
- Resource Requirements: Select a hosting plan based on your business needs, including server resources, storage space, and bandwidth.
- Security: The hosting provider should offer robust security measures to protect your data and website from potential attacks.
- Technical Support: Ensure the hosting provider offers quality technical support to help you address any issues that may arise.
- Price: Compare the prices of different hosting providers and ensure your choice aligns with your budget.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the hosting plan so that you can expand your website as your business grows.
- Backup and Recovery: Check the hosting provider’s backup and recovery options to ensure your data can be restored in case of unexpected situations.
- User Reviews: Read reviews and comments from other users to understand their experiences and choose a trusted hosting provider.
In summary, choosing a domain name and hosting that suits your business is a crucial step in establishing an online presence. A good domain name and reliable hosting can help you build a successful online business, providing stable website performance and a positive user experience.
2. Build a Website
When establishing an e-commerce website, you can choose from various platforms depending on your needs and budget. Here are some common e-commerce platforms:
- Shopify: Shopify is a highly popular e-commerce platform, offering a simple yet powerful solution suitable for startups and small to medium-sized businesses. It provides multiple templates, payment processing, order management, and more.
- WooCommerce: If you’re using WordPress to build your website, WooCommerce is an excellent plugin choice. It can transform your WordPress site into a feature-rich e-commerce platform.
- BigCommerce: BigCommerce is a comprehensive e-commerce platform providing robust tools for website building, marketing, order processing, and more.
- Magento: Magento is an open-source e-commerce platform, making it a good choice for businesses that require high customization. It offers extensive features but comes with higher technical requirements.
- Wix: Wix is a user-friendly website building platform that also offers e-commerce functionality. It’s suitable for small businesses and startups.
- Volusion: Volusion is a platform focused on e-commerce, offering many marketing and sales tools. It’s suitable for businesses in need of a complete solution.
- OpenCart: OpenCart is an open-source e-commerce platform providing basic e-commerce functions. It’s suitable for small to medium-sized businesses and users with stronger technical capabilities.
When choosing a platform, consider the following factors:
- Budget: Different platforms have different pricing models, so ensure you choose an option that aligns with your budget.
- Requirements: Consider your business needs, including the number of products, payment processing, order management, and marketing features.
- Technical Capability: Some platforms require more technical knowledge, so make sure to choose one that matches your technical skills.
- Scalability: Consider your business growth and choose a scalable platform to meet future needs.
- User Reviews: Read reviews from other users to understand their experiences with the platform.
Most importantly, choose an e-commerce platform that suits your business needs and goals, ensuring it can support you in building a successful online store.
The content above primarily emphasizes preparing to dive into e-commerce. In the next installment, we’ll walk you through the ins and outs of actually running an e-commerce venture, covering its growth and optimization.
Get Your Quote
Share details about your business, and we’ll tailor a solution for you!



2 Comments
Thank you for sharing
Your post offers practical solutions and strategies that readers can apply in their daily lives. It’s actionable and valuable. Thank you for sharing.